Slowness in web applications might be result of a wide range of underlying issues in the application code, client side, network or web server. Therefore, system administrators should analyze IIS logs, Failed Request Tracing logs, dump files, and HTTP.SYS logs to narrow down the issue.
Most of the time, the main focus during the troubleshooting is the server. Even if the server is not responsible of the issue, it may still provide valuable clues about the root cause.
In a slowness issue I worked on, these records in HTTPERR file took my attention:
2020-07-26 14:09:01 10.123.12.12 35316 10.12.123.123 80 - - - - - Timer_MinBytesPerSecond
2020-07-26 14:09:01 10.123.12.12 48012 10.12.123.123 80 - - - - - Timer_MinBytesPerSecond
2020-07-26 14:09:26 10.123.12.12 35350 10.12.123.123 80 - - - - - Timer_MinBytesPerSecond
2020-07-26 14:09:26 10.123.12.12 35356 10.12.123.123 80 - - - - - Timer_MinBytesPerSecondThese records show that the requests take more than 35 seconds to response due to a Timer_MinBytesPerSecond related issue.
What is MinBytesPerSecond?
It’s a parameter HTTP.SYS component uses to determine what speed is allowed while sending a response to the client. HTTPERR file references this parameter with Timer_MinBytesPerSecond keyword.
Here is the official description of this parameter:
Specifies the minimum throughput rate, in bytes, that HTTP.sys enforces when it sends a response to the client. The minBytesPerSecond attribute prevents malicious or malfunctioning software clients from using resources by holding a connection open with minimal data. If the throughput rate is lower than the minBytesPerSecond setting, the connection is terminated.
The current implementation only terminates the connection after the time it would have taken to stream the entire response back to the connecting client at the minimum bandwidth transfer rate has elapsed. If the transfer rate goes below the value specified by minBytesPerSecond only for a small period of time, but the overall transfer rate is higher, the connection will not be terminated.
The default value is 240.
Solution for Timer_MinBytesPerSecond related slowness issues
Based on the HTTP.SYS logs above, the root cause of the issue is the slow response throughput. The client is not receiving IIS response at a reasonable speed.
For Windows Server 2012 R2 (it was the server I worked on), IIS wants to send response at minimum 240 bytes per second. If the client is not able to receive it at this speed minimum, IIS terminates the connection. This logic prevents the server against slow HTTP attacks that may result in denial-of-service (DoS) situations (More on DoS attacks).
Here is what I recommend if you come across this issue:
- Check which clients are causing this issue
(You can proceed with the second step for a quick workaround and do this first step later)- The client machines might be in a slow network. If the issue is caused by the same client(s), you may be able to improve their condition to solve the issue
- Find out client IP addresses in the HTTPERR file and investigate their network as well as their OS
- Important: The client IP addresses in the file are unlikely to be the actual client machines. They are probably load balancer, proxy, or firewall addresses. First, find out which device these IPs belong to. For example, If they are load balancer addresses, check their logs to find out actual client IPs
- Remove the threshold for minimum response rate
- If the client IPs are legit (not malicious sources or possible attackers), set
minBytesPerSecondto0and monitor the system for a while - If the issue doesn’t happen again (you don’t see Timer_MinBytesPerSecond records in HTTPERR file), go back to this setting and play around the value (Try 500). It’s not recommended to set it 0 because it may make your application vulnerable to DoS attacks based on slow HTTP response
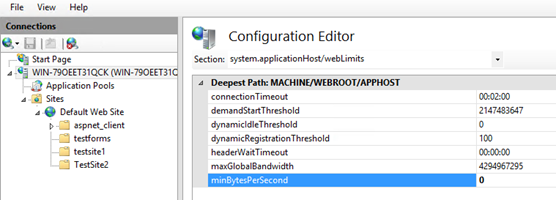
- Steps to change
minBytesPerSecond:- Go to IIS Manager. Click on the server name
- Double click on Configuration Editor
- Go to “system.applicationHost/webLimits”
- Set
minBytesPerSecondto0 - Reset IIS
- If the client IPs are legit (not malicious sources or possible attackers), set
If you want to change this parameter through web.config or application code, check this post out.
More about DoS attacks leveraging the slow HTTP responses: Prevent Slow HTTP POST vulnerability Denial of Service (DoS) attack